It’s imperative that we comprehend the effects of high heat brought on by climate change as temperatures are rising and heatwaves are occurring more frequently. It is commonly acknowledged that climate change is causing changes in weather patterns, increasing sea levels, and an increase in the frequency of extreme weather events. Unquestionably, there is a link between climate change and excessive heat because rising greenhouse gas emissions trap heat in the atmosphere, raising global temperatures.
Through comprehension, adaptation, and policy interventions, it is critical to address how severe heat affects people, communities, and the environment.
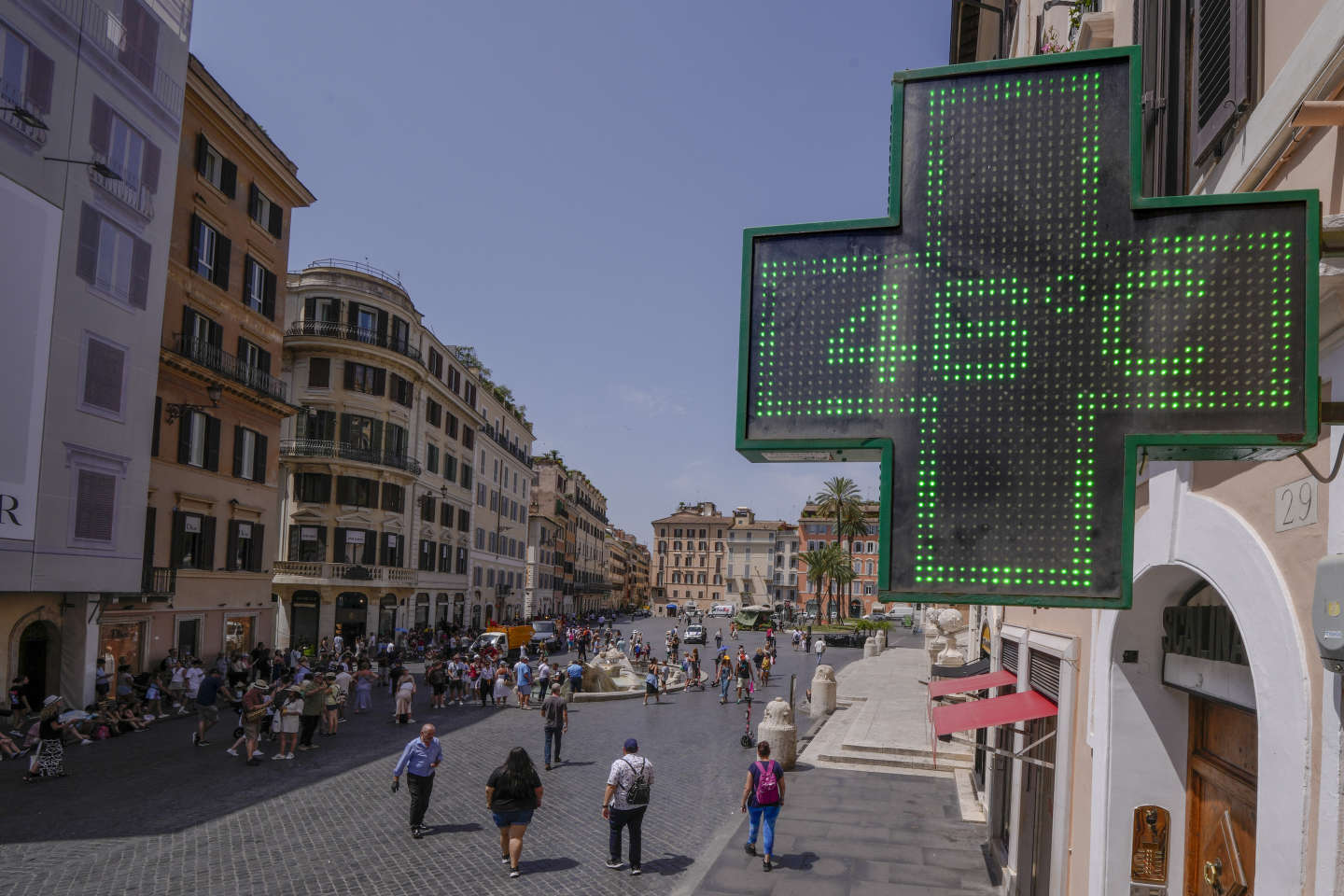
Long-lasting instances of extremely high temperatures that exceed the typical seasonal averages are referred to as extreme heat. The length and intensity of heatwaves, which are extended periods of extreme heat, set them apart from regular high temperatures. Numerous variables, including notably climate change, urbanization, and deforestation, contribute to the increasing frequency and severity of heatwaves.
Extreme heat can lead to serious health problems including heat exhaustion and heatstroke as well as make preexisting disorders worse. Heat-related illnesses have a disproportionately negative impact on vulnerable groups like the elderly, children, and low-income communities. Extreme heat has significant negative effects on the economy and society, including decreased productivity, increased energy usage, and infrastructural pressure.
People can take preventative measures to safeguard themselves during heatwaves, such as drinking enough of water, finding a cool place to hide out, and identifying the symptoms of heat-related sickness. Communities are key players in adaptation, putting into action solutions like heat emergency plans, building cooling facilities, and enhancing urban planning to lessen the impact of urban heat islands.
[FSM_featured_image size=full]
To combat excessive heat, policy interventions at multiple levels are necessary, including lowering greenhouse gas emissions and assisting with climate change mitigation measures.